Spring AOP
AOP in spring allows cross cutting of concerns. AOP is not dependent on Spring’s IOC container. The key unit of modularity in OOP(Object Oriented Programming) is the class, whereas in AOP the unit of modularity is the aspect. Spring AOP is implemented in pure java and hence does not require a separate compilation process
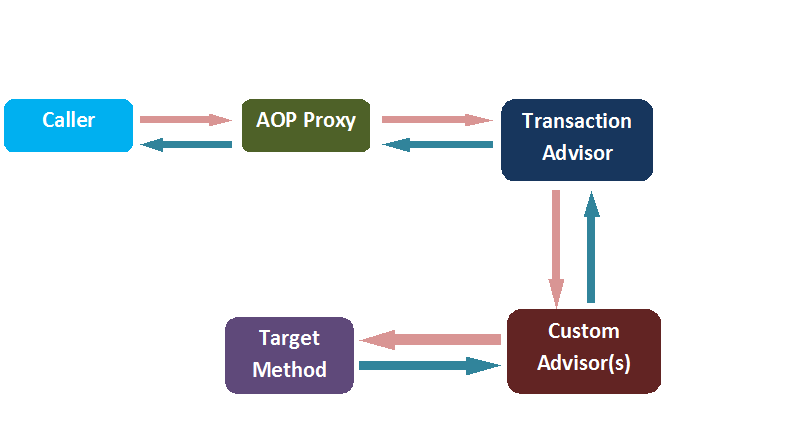
Aspect Oriented Programming (AOP) compliments OOPs in the sense that it also provides modularity. But the key unit of modularity is aspect than class.
AOP breaks the program logic into distinct parts (called concerns). It is used to increase modularity by cross-cutting concerns.
A cross-cutting concern is a concern that can affect the whole application and should be centralized in one location in code as possible, such as transaction management, authentication, logging, security
Where to use AOP?
• To provide declarative enterprise services such as declarative transaction management.• It allows users to implement custom aspects.
AOP Concepts
• Join point
Join point is any point in your program such as method execution, exception handling, field access etc. Spring supports only method execution join point.• Advice
Advice represents an action taken by an aspect at a particular join point. There are different types of advices:Before Advice: It executes before a join point.
After Returning Advice: It executes after a joint point completes normally.
After Throwing Advice: It executes if method exits by throwing an exception.
After (finally) Advice: It executes after a join point regardless of join point exit whether normally or exceptional return.
Around Advice: It executes before and after a join point.
• PointCast
It is an expression language of AOP that matches join points.• Introduction
It is an expression language of AOP that matches join points.• Target Object
It is the object i.e. being advised by one or more aspects. It is also known as proxied object in spring because Spring AOP is implemented using runtime proxies.• AOP Proxy
It is used to implement aspect contracts, created by AOP framework. It will be a JDK dynamic proxy or CGLIB proxy in spring framework.• Weaving
It is the process of linking aspect with other application types or objects to create an advised object. Weaving can be done at compile time, load time or runtime. Spring AOP performs weaving at runtime.AOP Implementations
AOP implementations are provided by:• AspectJ
• Spring AOP
• JBoss AOP
